Building a Kannada Physics Tutor LLM with Feynman-Style Explanations
Multi-stage fine-tuning pipeline to create a reasoning-first physics tutor in Kannada, combining domain-specific SFT and RAG for intuitive, grounded explanations.
Why This Project?
Most LLMs struggle with conceptual physics explanations in regional languages. I wanted to demonstrate:
Low-Resource Language
Teaching a model to think in Kannada, not just translate from English.
Feynman-Style Teaching
Intuitive, step-by-step reasoning with analogies—focusing on why, not just formulas.
Multi-Stage Pipeline
Language fluency → Domain reasoning → Factual grounding with RAG.
This case study demonstrates:
- End-to-end fine-tuning for low-resource languages + specialized domains
- How multi-stage SFT compounds improvements (language → domain → grounding)
- Complete evaluation pipeline: LLM-as-judge, quantitative metrics, qualitative analysis
System Overview
Goal: Given a physics question in Kannada (e.g., "How do we derive Laplace's equation for a membrane?"), generate:
- A step-by-step reasoning trace that builds intuition.
- A Feynman-style explanation in natural, fluent Kannada.
- Grounded answers using retrieved physics context (RAG).
Four-Model Progression
The training pipeline uses a staged approach where each model builds on the previous one:
1. Base Model
Gemma 3 1B — General-purpose LLM baseline (no specialization)
2. Kannada SFT
Language Foundation — Fine-tuned on general Kannada text for fluency
3. Physics SFT
Domain Reasoning — Physics concepts + Feynman-style explanations in Kannada
4. Physics + RAG
Factual Grounding — Retrieval-augmented generation with physics knowledge base
Why Multi-Stage Fine-Tuning?
Stage 1 (Kannada SFT): Teaches linguistic fluency and natural expression in Kannada, independent of domain.
Stage 2 (Physics SFT): Builds on fluency to add conceptual reasoning, derivations, and Feynman-style intuition.
Stage 3 (RAG): Adds factual precision by retrieving relevant physics context before answering, preventing hallucinations.
LLM-as-Judge Evaluation
Each model's output is evaluated using an LLM-as-judge with a structured grading prompt. The judge scores answers on a 0–5 scale based on:
Physics Correctness
Conceptual accuracy and mathematical precision
Reasoning Quality
Step-by-step clarity and logical flow
Kannada Fluency
Natural language quality and proper grammar
Contextual Relevance
Answers the specific question with appropriate detail
All scores were collected in a CSV file and visualized using score distributions and boxplots to show the progressive improvement across the 4-model pipeline.
Quantitative Evaluation
I evaluated all four models on a held-out set of physics questions, scoring each output with an LLM-as-judge (0–5 scale).
Score Distribution by Model
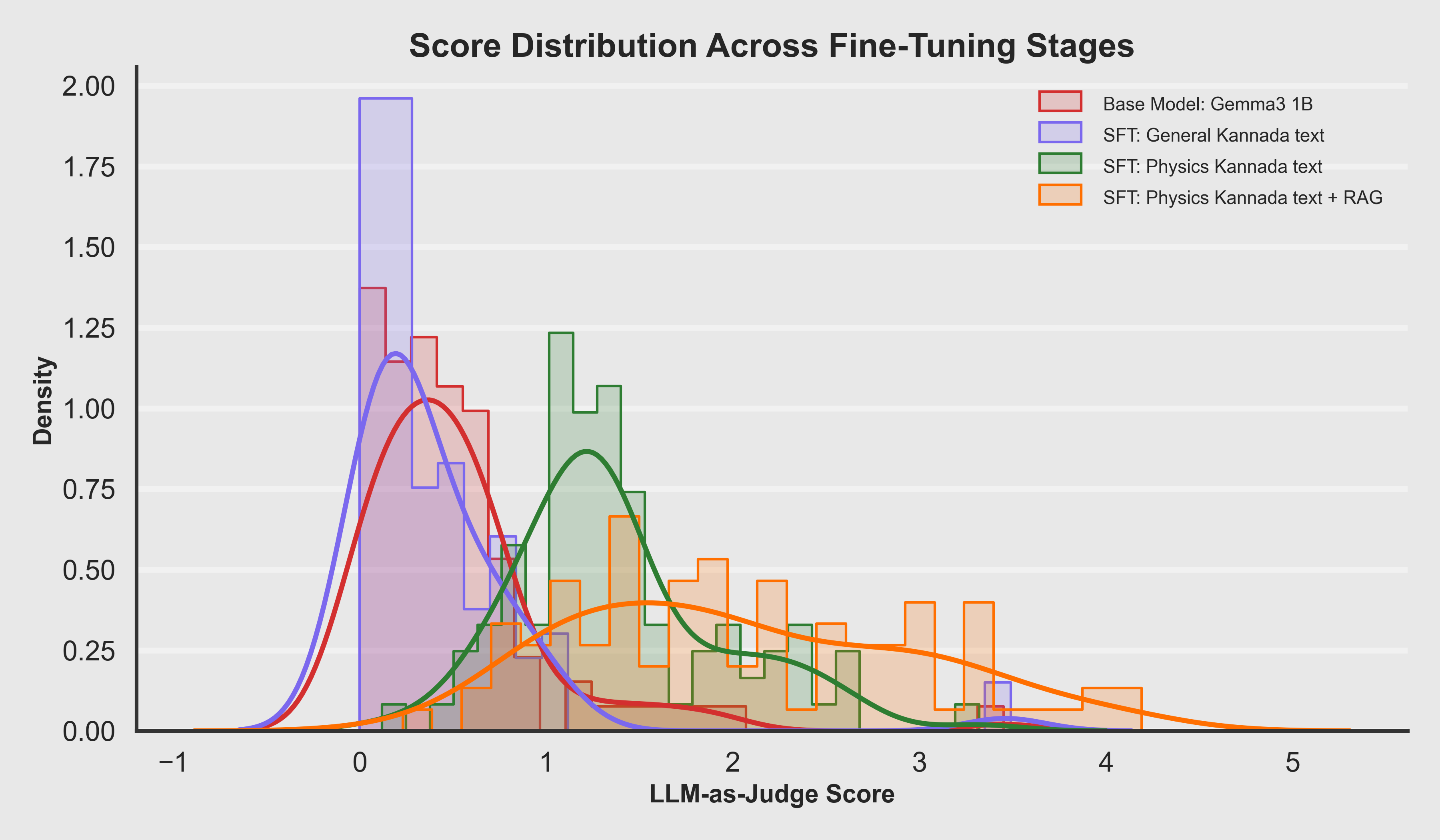
- The Base Model shows very low scores (mostly 0–1), indicating poor physics understanding and Kannada fluency.
- Kannada SFT improves language quality slightly but still lacks physics reasoning—scores remain low.
- Physics SFT shows a dramatic shift—the distribution moves to mid-range (2–3), reflecting strong conceptual reasoning.
- Physics + RAG achieves the highest scores (3–4), with factual grounding preventing errors and hallucinations.
The progressive right-shift in score distributions demonstrates that each stage adds measurable value: fluency → reasoning → grounding.
Boxplot Comparison
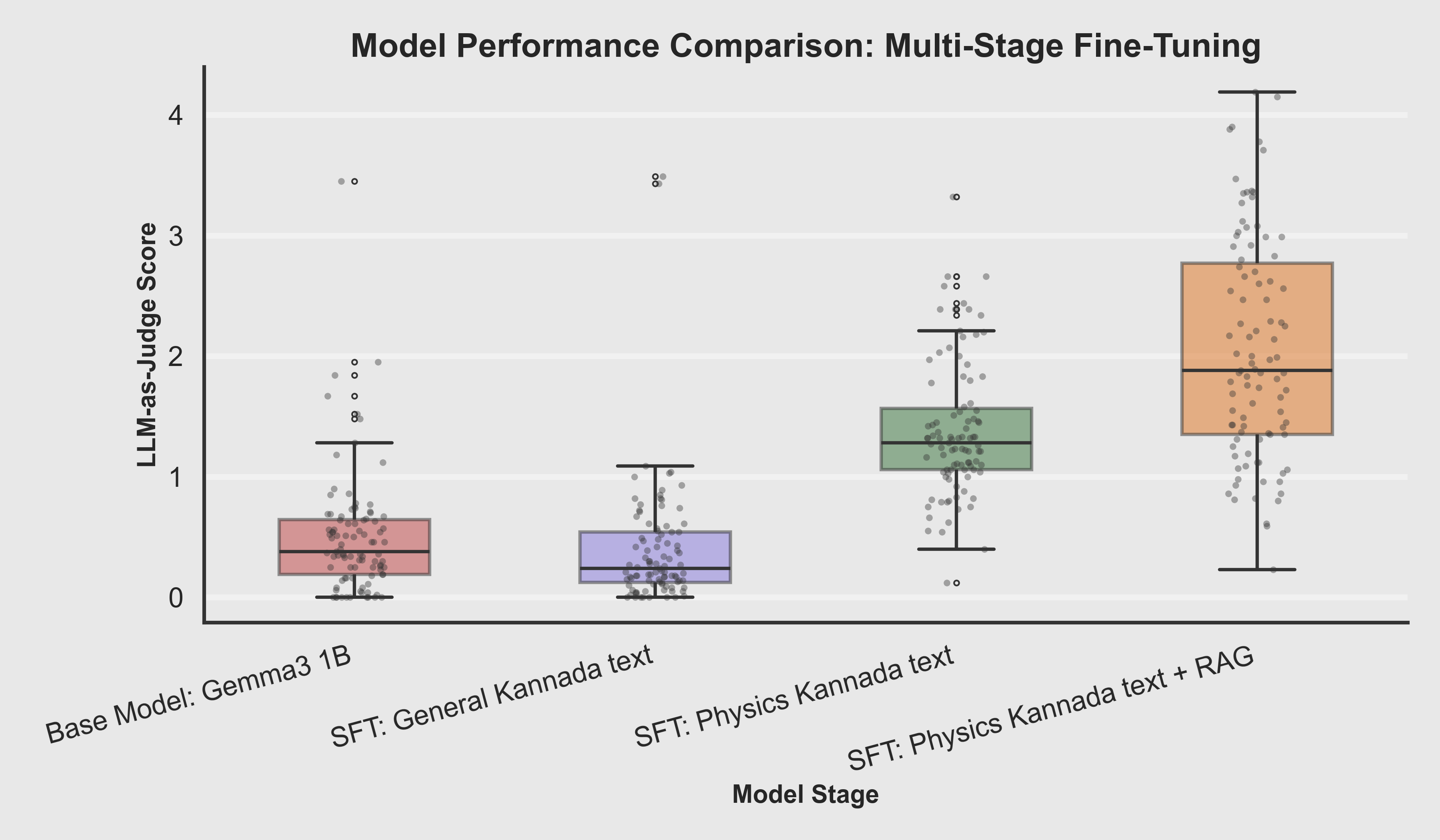
- Median score increases dramatically from Base (near 0) → Kannada SFT (0.5) → Physics SFT (2.3) → RAG (3.7).
- The interquartile range narrows for Physics SFT and RAG models, showing more consistent performance.
- Low-score outliers become rare in the final RAG model, indicating reliable quality across diverse questions.
Key Takeaway: Multi-stage fine-tuning doesn't just improve average performance—it systematically reduces failure modes and increases reliability.
Hero Examples
Compare the output of all four models. Notice the progressive improvement: Base → Kannada SFT (fluency) → Physics SFT (reasoning) → Physics + RAG (grounding). Each model column includes analysis showing what each stage contributes.
Model Comparison
Curl of Vector Field
ಅತಿ ಸೂಕ್ಷ್ಮ ಚದರದ ಸುತ್ತಾಟ ಮತ್ತು ವೆಕ್ಟರ್ ಕ್ಷೇತ್ರದ curl ನಡುವೆ ಇರುವ ಸಂಬಂಧವೇನು?
What is the relationship between rotation of an infinitesimal area element and the curl of a vector field?
Analysis
The base model largely fails to understand the question and produces text that is vague and only partly in Kannada.
Analysis
After general Kannada SFT, the model becomes much more fluent, but it still lacks the domain knowledge needed to explain curl or area-element rotation. That's expected—general SFT teaches language, not physics.
Analysis
The breakthrough comes with Physics SFT, where the model is fine-tuned on a curated dataset of physics reasoning and Feynman-style explanations. Here, the model finally explains curl as a measure of rotational tendency—a core conceptual idea. The answer becomes structured, relevant, and intuitively meaningful.
Analysis
The RAG-enhanced model then adds authoritative factual grounding by retrieving the correct physics context before answering. The result is a clean, mathematically correct, intuitive explanation fully in Kannada—exactly what a human physics tutor would say. This demonstrates how SFT improves fluency and reasoning patterns, while RAG ensures factual precision.
Click on a column to highlight it. The progression shows: language fluency → domain reasoning → factual grounding.
Detailed Training Specifications
Training Pipeline Overview
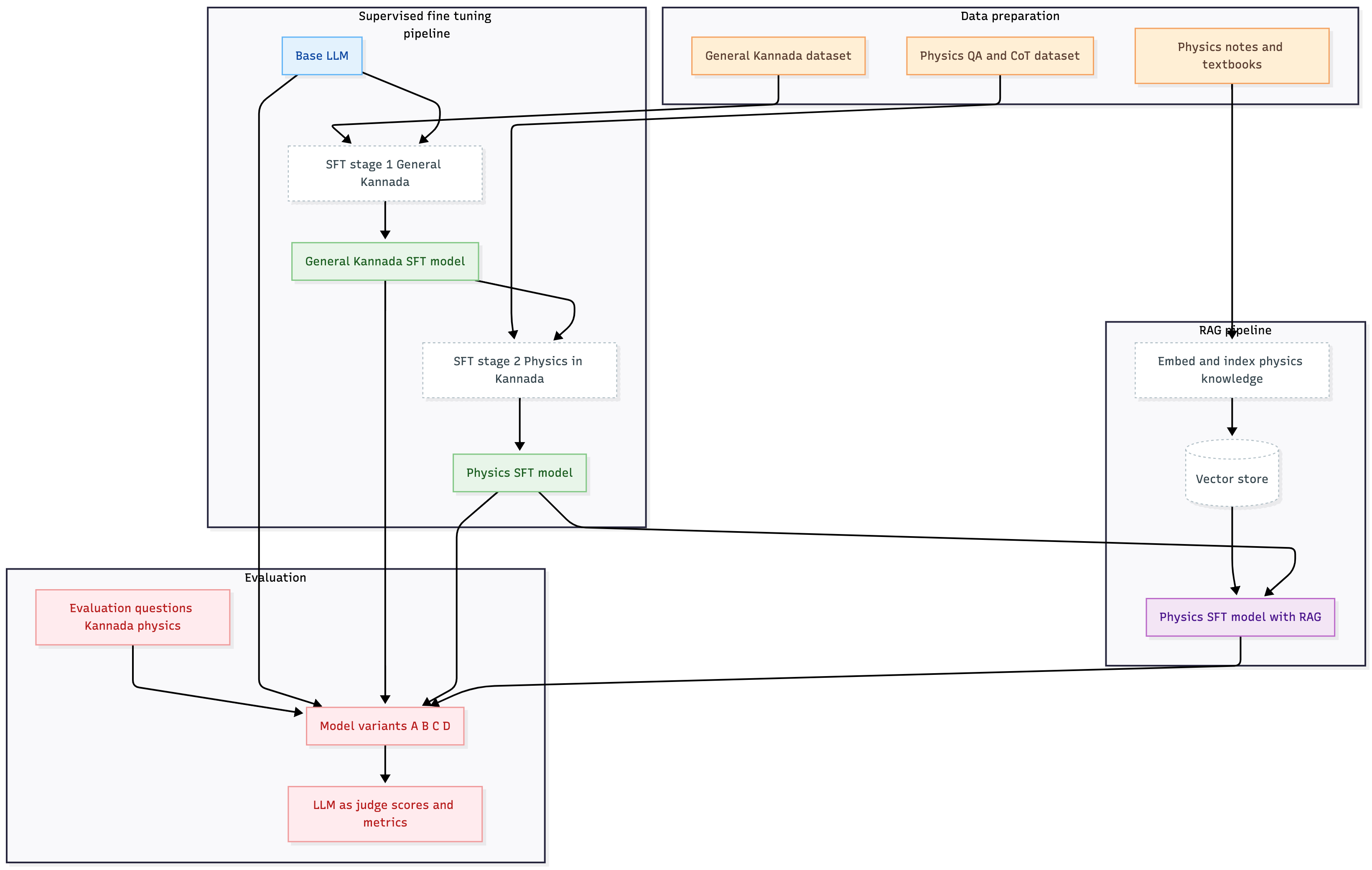
The complete training pipeline flows from a base open-source model through two stages of SFT (Kannada language → Physics reasoning) and finally RAG integration for factual grounding. Each stage builds on the previous one to compound improvements.
Data Preparation
Base Model
Kannada SFT Data
General Kannada text corpus (news, essays, conversations)
Physics SFT Data
Custom physics Q&A with Feynman-style reasoning traces in Kannada
RAG Knowledge Base
Physics textbook chapters in Kannada (vector store)
Feynman-Style Reasoning Trace Structure
The Physics SFT dataset includes structured reasoning traces that teach the model to think like Feynman—building intuition before formulas. Each training example follows this 8-step approach:
Identify Core Idea
State the simplest underlying principle of the concept.
First Principles Reasoning
Break down the idea into its most basic elements, avoiding jargon at first.
Analogies & Everyday Examples
Relate the concept to familiar, tangible experiences (blocks, water, children's games, etc.).
Curiosity Hooks
Ask playful or intriguing questions that spark further interest ("Why should nature behave this way?")
Progressive Depth
Gradually increase rigor—from intuition → simple mathematics → abstract reasoning—always showing why each step matters.
Cross-Connections
Show how this idea connects to other areas of physics or science.
Humility & Limits
Acknowledge approximations, open questions, or where the laws might break down.
Engagement & Clarity
Keep the tone conversational, clear, and inspiring—as if talking to bright but curious students.
Impact: This structured approach trains the model to not just recite formulas, but to build genuine conceptual understanding—teaching why physics works, not just what the equations are.
Training Configuration
Hardware
- GPU: 1x A40 (48 GB VRAM)
- Framework: PyTorch with HuggingFace Transformers
Stage 1: General Kannada SFT
Training Steps: 80
Epochs: 1
Batch Size: 8
Max Learning Rate: 5e-5
Initial Training Loss: 4.709
Final Training Loss: 2.898
Final Eval Loss: 2.912
Eval Interval: Every 5 steps
Trained on diverse Kannada text to establish language fluency and natural expression patterns.
Stage 2: Physics Kannada SFT
Training Steps: 90
Epochs: 1
Batch Size: 8
Max Learning Rate: 5e-5
Initial Training Loss: 3.248
Final Training Loss: 2.448
Final Eval Loss: 2.474
Eval Interval: Every 10 steps
Fine-tuned on custom physics Q&A with Feynman-style reasoning traces, teaching conceptual understanding and step-by-step derivations.
Training Progression:
- Stage 1 reduced eval loss from 4.71 → 2.91 (38% reduction)
- Stage 2 further reduced eval loss from 3.25 → 2.47 (24% reduction)
- Healthy train/eval gap indicates good generalization without overfitting
- Cosine learning rate schedule with warmup for stable optimization
Key Learnings
Low-Resource Language Fine-Tuning
Separating language fluency (Kannada SFT) from domain knowledge (Physics SFT) allows the model to learn each skill independently before combining them. This staged approach is more effective than trying to learn both simultaneously.
Multi-Stage SFT Compounds Benefits
Each stage adds measurable value: language quality → reasoning patterns → factual accuracy. The boxplots clearly show that each stage shifts the performance distribution upward.
RAG as a Grounding Layer
Fine-tuned models can reason well but may still hallucinate details. Adding RAG (retrieving relevant physics context before generation) dramatically improves factual accuracy without additional training.
LLM-as-Judge for Evaluation
Building a complete evaluation pipeline with LLM-as-judge, quantitative metrics (distributions, boxplots), and qualitative analysis provides a full picture of model capability—essential for demonstrating product viability.
From Demo to Product: AI-Powered Physics Education for Rural India
This trained model demonstrates the foundation for a scalable educational platform—a system designed for government schools and rural communities across India where students often lack access to quality STEM education in their native language.
Instead of replacing teachers, this platform acts as an always-available AI tutor that supplements classroom learning, provides personalized explanations, and helps students build deep conceptual understanding in their mother tongue—whether it's Kannada, Hindi, Tamil, Telugu, or any of India's 22 official languages.
The Challenge in Rural India
🏫Language Barrier
In rural Karnataka, 85% of students study in Kannada-medium schools, but most quality educational resources (textbooks, videos, tutoring) are only available in English. This creates a fundamental comprehension gap in STEM subjects like Physics.
👨🏫Teacher Shortage
Government schools face chronic shortages of qualified physics teachers. Many schools share one teacher across multiple subjects or grades, leaving little time for conceptual depth or individual student attention.
📚Rote Learning Culture
Traditional teaching emphasizes memorizing formulas and procedures without understanding. Students can solve textbook problems but struggle to explain why physics works—exactly what Feynman-style teaching addresses.
💰Cost of Private Tutoring
Private physics tutoring costs ₹3,000-5,000/month ($35-60)—unaffordable for families earning ₹15,000/month. This creates an educational divide where only urban, affluent students get quality conceptual teaching.
Product Architecture: Multi-Agent AI Tutor System
Concept Explainer Agent
Feynman-Style Intuitive Teaching
This is where our Physics+RAG model powers the system. When students ask physics questions, this agent generates Feynman-style explanations with analogies, step-by-step reasoning, and visual intuition.
Student Input
- • Voice or text questions in Kannada
- • "I don't understand why..." prompts
- • Follow-up clarifications
Agent Output
- • Conceptual explanations in Kannada
- • Real-world analogies (village examples)
- • Progressive depth (intuition → math)
Practice Problem Generator
Adaptive Problem Sets & Step-by-Step Solutions
Generates contextually relevant practice problems based on the student's current chapter and difficulty level, with detailed worked solutions that teach the problem-solving approach.
Features
- • Chapter-aligned problem generation
- • Difficulty progression (easy → hard)
- • Culturally relevant scenarios
Student Benefits
- • Unlimited practice questions
- • Instant feedback on approach
- • Learn from worked examples
Learning Path Advisor
Personalized Curriculum & Gap Analysis
Tracks student progress across chapters, identifies conceptual gaps, and recommends targeted review topics before moving to advanced concepts.
Analytics Tracked
- • Weak vs. strong concept areas
- • Time spent per topic
- • Question accuracy patterns
Adaptive Actions
- • Suggest prerequisite review
- • Adjust difficulty dynamically
- • Recommend practice focus areas
Exam Preparation Coach
Board Exam Focused Support
Provides targeted support for Karnataka SSLC (10th) and PUC (12th) board exams, including previous year question analysis, common mistake patterns, and exam strategy guidance.
Exam Focus
- • Previous year papers (2015-2024)
- • High-weightage topic identification
- • Marking scheme understanding
Strategic Prep
- • Mock tests with scoring
- • Answer writing practice
- • Time management strategies
Why This Becomes a Viable Social Enterprise
🌍Multi-Language Scalability
The same multi-stage fine-tuning approach (General Language SFT → Physics SFT → RAG) can be replicated for Hindi, Tamil, Telugu, Marathi, Bengali, and other regional languages. Train once per language, deploy nationwide. Start with Kannada (6 crore speakers), then expand to Hindi (55 crore speakers) for massive impact.
📱Mobile-First, Offline-Capable
Deploy lightweight models (1B-3B parameters) that run efficiently on mobile devices. Students can download chapter-specific models and knowledge bases for offline use—critical for rural areas with unreliable internet. Voice input removes typing barriers for students uncomfortable with keyboards.
💡Proven Pedagogy + AI Scale
Feynman's teaching method is proven effective but relies on rare, exceptional teachers. By encoding this pedagogy into fine-tuned models, we democratize access to world-class physics teaching. Every student, regardless of location or family income, gets a patient, always-available tutor who explains concepts intuitively.
🎯Sustainable Revenue Model
Freemium approach: Basic concept explanations free for all students. Premium features (adaptive practice, exam prep, learning analytics) at ₹99/month ($1.20)—affordable even for low-income families. Government partnerships and NGO sponsorships subsidize access for students below poverty line. B2B licensing to private coaching centers.
Path to Impact at Scale
Pilot in 50 Karnataka Government Schools (Year 1)
Partner with Karnataka State Education Department. Deploy in 50 rural high schools (~25,000 students). Track learning outcomes: concept test scores, board exam performance, student engagement metrics. Gather teacher and student feedback for product iteration.
Expand to All Karnataka Schools (Year 2)
Scale to all 10,000+ government high schools in Karnataka (~2.5 million students). Launch premium tier for parents who want advanced features. Begin training models for Hindi, Tamil, and Telugu based on the proven Kannada pipeline.
National Rollout Across India (Year 3-5)
Launch in other states with regional language models. Partner with central government initiatives like Digital India and National Education Policy 2020 (which emphasizes mother-tongue education). Target: 50 million students across 10+ languages. Expand to Chemistry, Math, and Biology using the same SFT+RAG architecture.
Continuous Improvement via RLHF
Collect student ratings on explanations ("Was this helpful?"). Track which analogies work best for different concepts. Use this feedback for reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) to continuously improve explanation quality. Models learn to adapt teaching style based on what resonates with Indian students.
From Technical Demo to Social Impact Startup
This case study proves the foundational technology works: we can fine-tune models to teach complex STEM concepts intuitively in low-resource languages, evaluate quality rigorously, and ground explanations with RAG to prevent hallucinations.
The product layer—multi-agent tutoring, mobile-first delivery, exam preparation support, and teacher dashboards—transforms this technical capability into a scalable social enterprise. The goal isn't to replace teachers; it's to empower every student in rural India with a personalized physics tutor who speaks their language and teaches like Feynman—bridging the educational divide between urban privilege and rural potential.